|
Puncture Wound
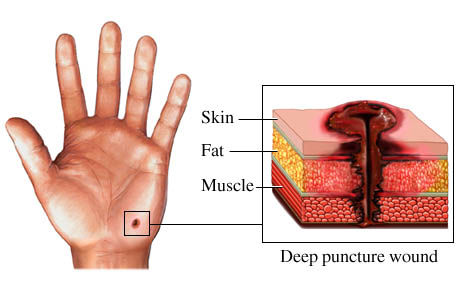 First,
check to see that nothing is left in the wound. First,
check to see that nothing is left in the wound.
Check to see if the object that caused the
wound is intact. If a piece is missing, it may be stuck in the wound.
Allow the wound to bleed freely, but if
bleeding is heavy or squirting out, apply pressure until it stops.
If bleeding won't stop, you will need
emergency care.
The basics of wound care
- Stop the bleeding:
Minor puncture wounds and cuts usually stop bleeding on their own. If not,
apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth or bandage. If the blood spurts or
continues after several minutes of pressure, emergency care is necessary.
- Clean the wound:
First, wash your hands. If your hands are not clean, you may spread bacteria
into the wound. Cleanse the wound. Wash with water. You can use a mild soap
such as Ivory if the wound is very dirty. If dirt or debris remains in the
wound, clean a pair of tweezers with alcohol and remove the dirt. If you
cannot get the dirt or debris out, contact your doctor.
- Protect the wound: An
antibiotic ointment such as Neosporin or Polysporin can be used. Apply a thin
layer over the wound. This will help coat and protect the wound. Large
amounts of ointment are not helpful because they can attract bacteria. Apply
the ointment with a clean swab or gauze. Do not apply directly from the tube
in order to avoid contamination of the tube. Ointments can be applied up to 3
times a day, but you should always clean the wound before applying ointment.
- If the puncture is
over a joint and there is pain on movement of the joint, it must be evaluated
at the hospital. Surgery may be required to fix any damage.
- Puncture wounds from
human or animal bites need medical treatment and often need antibiotics.
Medical Treatment
The wound will be thoroughly cleansed.
The doctor may use instruments to look for objects in the wound. You may be
given a tetanus shot if more than five years have elapsed since last dose.
Antibiotics may be given to people with diabetes, peripheral vascular disease,
contaminated wounds, or deep wounds to the foot. Most healthy people without
signs of infection do not require antibiotics.
-
First Aid Case List -
back to top - |
 First,
check to see that nothing is left in the wound.
First,
check to see that nothing is left in the wound.